Radon is a radioactive gas occurring naturally as a decay product of radium. As it decays, radon produces new radioactive components called radon daughters or decay products. Unfortunately, human feelings cannot recognize radon and radon daughters because they are colorless, odorless, and tasteless.
Table of Contents
Where Does Radon Come From?
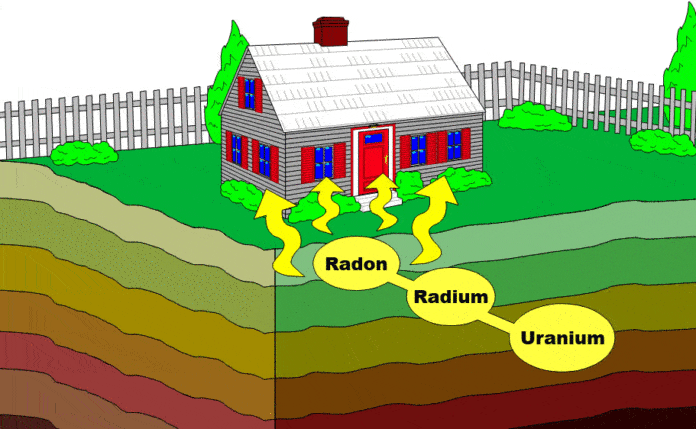
Radon arises in the ground and can be located in soil and rocks. As with any gas, radon disperses as it flows along the way of least resistance to the ground’s surface before accessing the atmosphere.
Once it enters the atmosphere, radon becomes weakened in the outdoor air, and concentrations are so mean that it is of secondary concern.
Radon can also move into any airspace, such as basements, crawl areas, or caverns. Once inside an enclosed place, such as a home, radon can accumulate.
For this reason, indoor concentrations usually are higher than those obtained outdoors. Houses with limited air exchange because of changes to prevent heat loss will usually have higher indoor radon levels than draftier houses.
How Does Radon Get Into Homes?
Radon passes through tiny spaces in the soil and rock on which a house is built and can flow into a home through dirt floors; floor drains, sump pits, joints, or tiny cracks and pores in hollow-block walls. As a result, radon collections are higher in the lower levels of a home, such as a basement.
Radon can dissolve in freshwater and add to airborne radon in homes when released within running water.
Investigations show that very few public groundwater groceries contain enough radon to be a significant radon source in homes.
There is very little radon in surface water supplies because the water is exposed to outdoor air, thus reducing the radon concentrations.
Is Radon Harmful Indoors?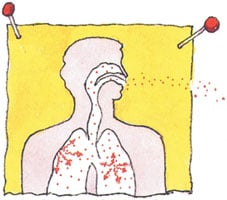
When radon experiences a radioactive crack up, it turns into other radioactive elements called radon daughters. Radon daughters are masses, not gasses, and stick to surfaces such as dust particles in the air.
These particles can adhere to the lung’s airways if polluted dust is inhaled. As these radioactive dirt particles split down further, they release tiny bursts of energy, harming lung tissue and increased lung cancer risk. In general, the risk rises as the radon level and the exposure length increase.
Radon itself is chemically stable, and a breathed radon atom is likely to be exhaled before it collapses. Thus, the main health risk from radon is exposure to its decay products.
What Can Be Done To Decrease Exposure To Indoor Radon?

Radon can be reduced with various methods. Some methods are simple, while others are complex and expensive. Each method’s effectiveness will depend on each house’s individual features, the radon level, the radon entry maps, and how completely a job is done. No one can promise that these systems will work as they did in the test houses.
It would help if you did radon testing to define the level to which radon has been reduced. If the radon levels have not been adequately lowered, further reduction steps may be taken, and the testing process repeated. All tests should be done the same way as the test confirming your house’s high radon levels.
- Air Purifiers remove particles such as dust or radon decay products from the air. To eliminate radon, you should choose a powerful air purifier with an advanced filtration system and a carbon filter.
- Natural ventilation. Use your windows to ventilate your home. Radon-laden indoor air replaces with outdoor air and neutralizes pressure.
- It would help if you ventilated the lowest level of your home, where it is in close contact with the main source of radon; the soil. If you have a basement, that is the space to ventilate. If your house sits on a concrete slab, then your alternative is to ventilate the living area. Opening windows throughout all levels of your house is recommended.
- Forced Ventilation. Forced air fans can provide a controlled volume of required ventilation. For example, a fan could be installed to continuously blast fresh air into the house through the existing primary forced-air heating, ducting, and supply records with windows and doors remaining closed. Alternatively, fans could exhale air into the house through protected intakes through the house’s surfaces or mounted in windows. A fan could also be installed to blow outdoor air into a crawl space.
- Sealing Cracks and Openings. If possible, the openings in the top row of concrete slabs in the basement walls should be tied with mortar or urethane foam: seal the wall and floor joint with elastic polyurethane membrane sealants. Cracks and utility breaks should be increased enough to allow filling with compatible, gas-proof, non-shrinking sealants. Porous surfaces (significantly block walls) need the application of waterproof paint, cement, or epoxy to a carefully-prepared surface.
- Drain water away from the foundation.
- Sub-Slab Suction. The radon can be moved from below the slab and discharged away from the house.
- Block-Wall Ventilation. Moves radon from the areas within a concrete block wall before it can access the house or drives air into block walls so that radon is stopped from entering the walls.
- Prevention of House Depressurization. Some exhaust fans and combustion units (such as wood stoves and fireplaces) can decrease your house’s air pressure by applying air and exhausting it outside. The lower the air pressure in your home, related to that in the soil, the more radon-laden air can be moved inside from the underlying soil.
- House Pressurization. Controls that part of the house, which is connected with the soil at a pressure more significant than the air in the soil. This limits soil gas, including radon, from entering the home. The most typical application of this method is to blow upstairs air into the basement.
How To Test Your Home for Radon?
1) buy a radon testing kit. You don’t need professional devices. Instead, you can take a low-cost DIY (Do It Yourself) radon test kit. Whatever radon test kit you buy, make sure it matches the EPA specifications.
2) Close doors and windows at least 10 hours before the testing period to get the best results.
3) Radon test kit should be stored at the lowest level of your home. That could be a basement or the first floor. Next, pick a room you use daily, such as the living room or bedroom.
Of course, every radon test kit will include all the necessary information to do the test. Could you read it before you start?
If you don’t want to do it yourself, you can hire a professional to do it for you. But, of course, it will be more expensive.